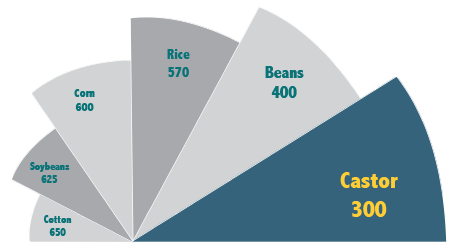
Sowing castor bean in the second season
Immediately profitability and benefits for next crops.
Kaiima
Kaiima Seeds is a castor genetics and breeding company that develops innovative castor hybrids improving plant productivity on a large scale and in modern agricultural systems.
The CastorMaxx© platform is an industry-leading castor production system that drives castor productivity to new heights. CastorMaxx© hybrids offer game-changing yield and benefits to growers. The platform is supported by experts in breeding, crop management and research aimed at customizing castor farming to fit the needs of each single market.
Kaiima is committed to developing new, pioneering solutions that sustainably improve the global production of food, feed, feedstock, bio-based oil and oil by-products.

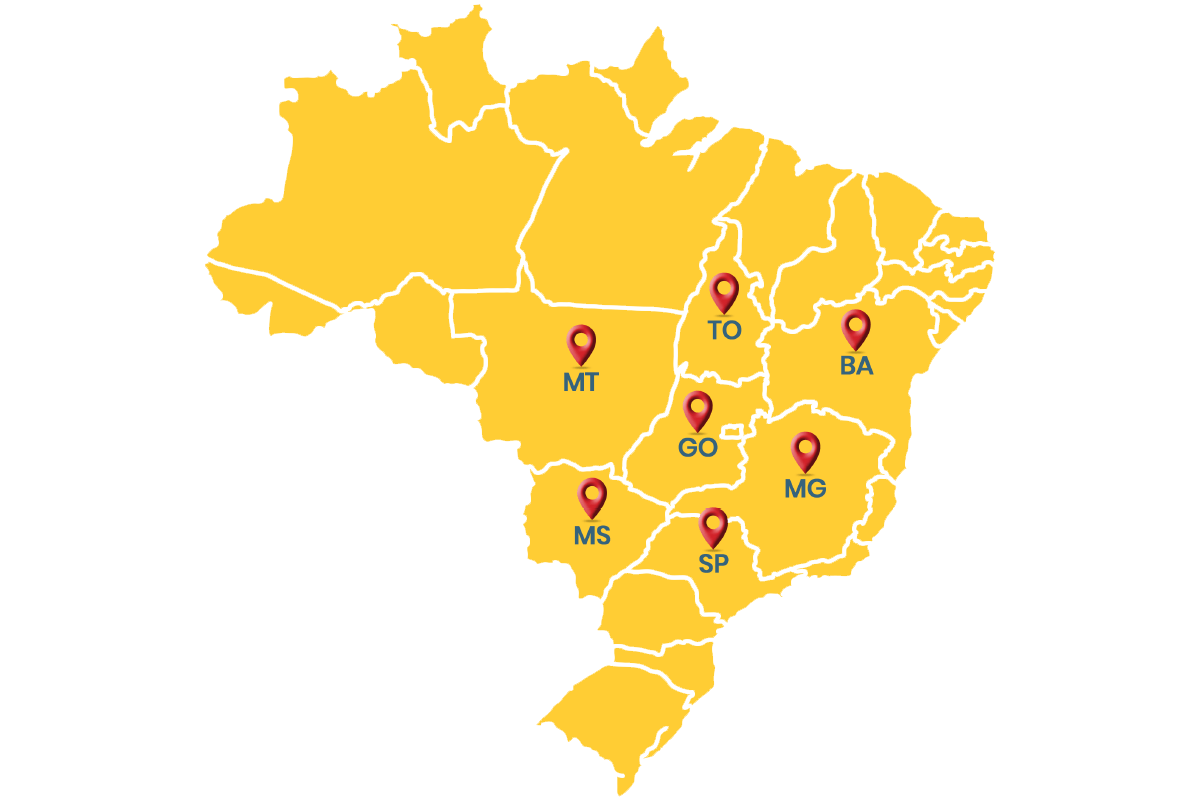
Where we are

The castor Bean Crop
Ricinus communis, the castor bean, is a species of flowering plant of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae. It is the sole species of the monotypic genus, Ricinus, and subtribe, Ricininae.
Castor is native from the south-eastern Mediterranean Basin, Eastern Africa and India, although it is widespread throughout tropical regions.
Castor seed is the source of castor oil, which has a wide variety of uses. The seeds contain high percentage of oil that is rich in triglycerides, mainly ricinolein. The seed also contains ricin, a water-soluble toxin, which is also present in lower concentrations all over the plant.
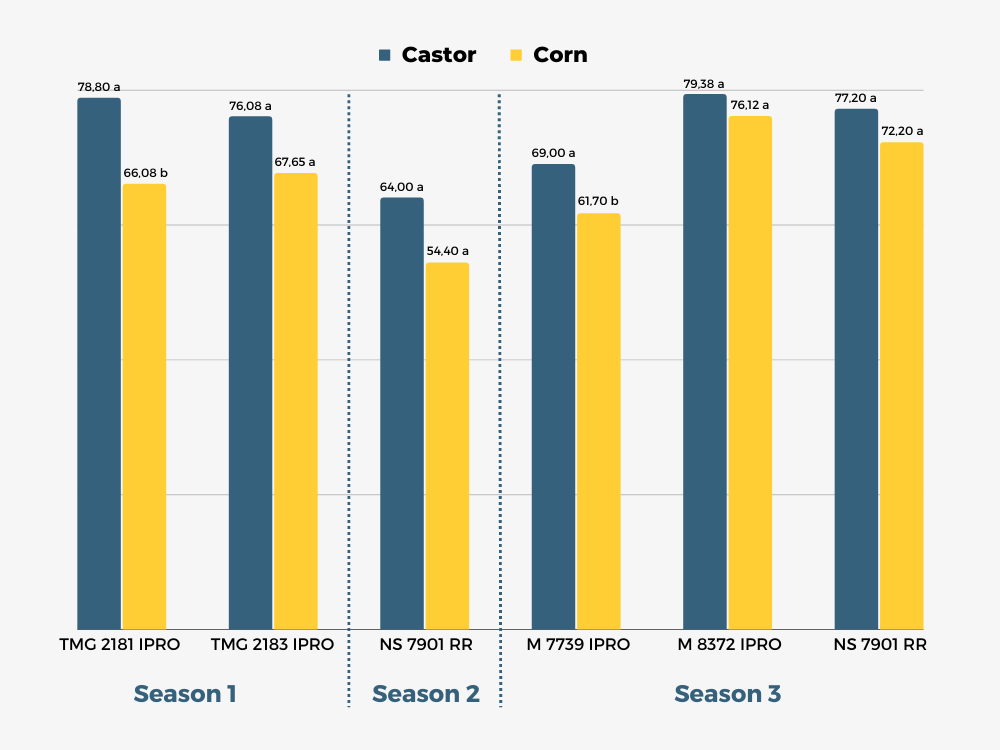
Castor bean: potential for high profitability for the second season – safrinha
Crop Benefits
Castor bean: potential for high profitability for the second season
Besides being an excellent option for the crop rotation due to its agronomical benefits (as seen below), castor can provide high profitability potential to growers.
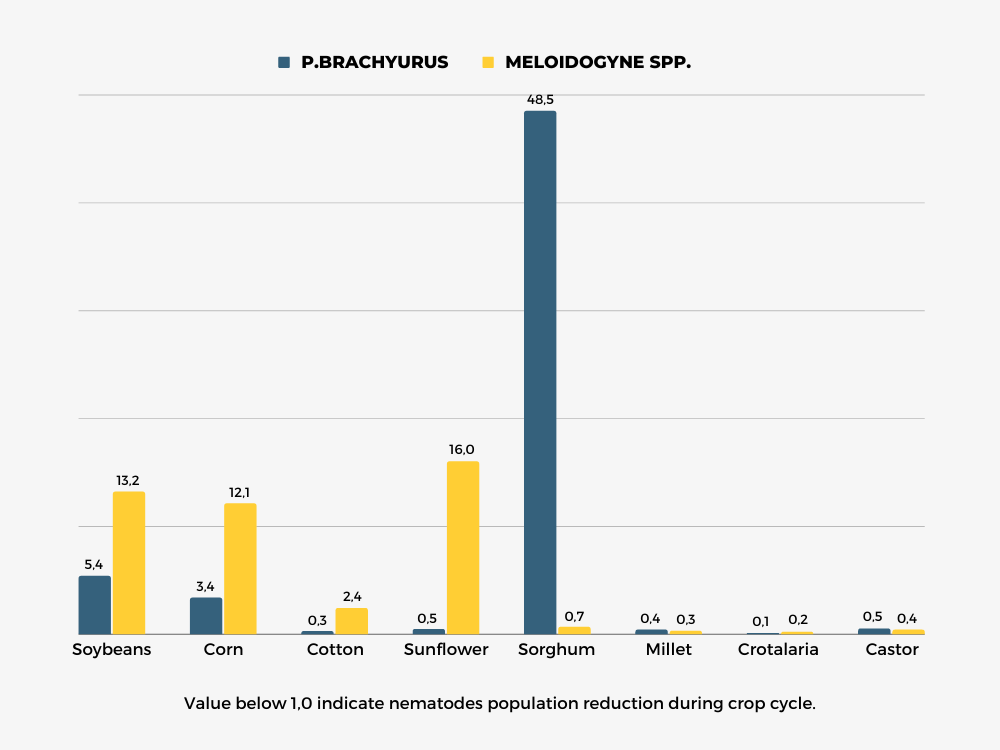
Nematode Control
Soil Regeneration

Root characteristics:
- Pivotal;
- Strong;
Allows compacted soil management with potencial yield benefit for subsequent crops in the same area.
Water management
Lowest water demand in the entire crop cycle with lower yields risk compared to other crops.